What exactly is marijuana, and why has it become such a big topic? Understanding the facts helps you cut through all the noise and mixed messages.
Marijuana is a plant that contains chemicals called THC and CBD - THC is what makes people feel high.
Marijuana is a plant composed of over 60 naturally occurring chemicals called cannabinoids1. The two most well-known cannabinoids are CBD and THC.
CBD is short for cannabidiol. It’s the chemical compound in marijuana that can be isolated and used for many medical purposes. On its own, CBD doesn’t make people feel high.
The other well-known component of Marijuana is THC. THC is short for tetrahydrocannabinol. It’s the primary psychoactive cannabinoid found in marijuana. THC is the part of Marijuana that makes you feel high, often described as happy and relaxed.
Common Names
- Pot
- Weed
- Green
- Grass
- Mary Jane
- Ganja
- Skunk
- Hashish
- Hash
- Reefer
- Herb
- Cannabis
- Blunt

Marijuana, also known as cannabis, has been around for thousands of years. The plant originally grew wild in Central Asia and parts of China.
Ancient people discovered they could use it to make rope and cloth, while others found that certain parts had effects on how they felt. Over time, people began growing cannabis in many different parts of the world.
Marijuana has been used for medicinal purposes for more than 3,000 years, though little research has been conducted on its effectiveness. There is some research on its impact to treat pain, nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy, and some muscle issues caused by multiple sclerosis.
THC, the psychoactive chemical in marijuana, turns off inhibitory neurotransmitters, which regulates how much dopamine our body gets. The regulator removal allows for the free flow of dopamine, which makes you feel good, and the surge of dopamine is the high.
As with all substances, marijuana use in adolescence heightens the risks because of the important brain development happening during those years. Substantial evidence shows that teens who use marijuana can develop cannabis use disorders as teens and are more likely to as adults.3 Marijuana use can cause changes in the brain that lead to addiction because the brain becomes accustomed to the large amount of dopamine released by the THC. After excessive use of marijuana, one can feel that they need to get high in order to feel “normal.” This is called dependence and can lead to addiction.4
Marijuana looks like a green plant with leaves that have several pointed sections, almost like fingers on a hand. The parts people use most are the dried flowers or buds, which are usually green or brown and can look leafy or chunky.
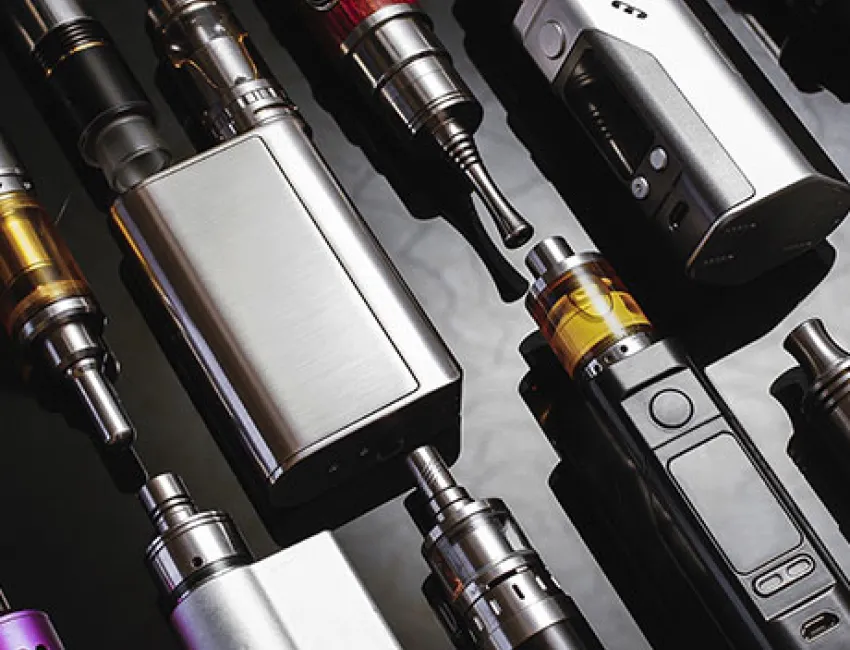
Today, marijuana comes in many forms - from oils and wax-like concentrates to edibles that look like regular candy, gummies, or baked goods, and even in vape pens that can look just like regular e-cigarettes.
THC, the psychoactive chemical in marijuana, turns off inhibitory neurotransmitters, which regulates how much dopamine our body gets. The regulator removal allows for the free flow of dopamine, which makes you feel good, and the surge of dopamine is the high.
Smoking, vaping - The most typical form of usage includes joints, pipes, bongs or vaporizers, which uses a battery to heat the marijuana in order to release the active ingredients.
Eating, drinking - The effects of edibles, teas and sodas can take longer to be felt, because absorption of THC through the stomach takes longer than it does when it is smoked or vaped. This may cause people to consume too much. It can take up to four hours to feel the full effects. This form also lasts longer than smoking, even up to ten hours.
Dabbing - A dab is THC extracted from marijuana. A dab normally contains up to 60-80% THC. The high is more intense due to the potency (strength) of THC but the dangers of dabbing are unknown.
The Effects of Marijuana
- Trouble thinking, remembering, learning
- Anxiety, paranoia, delusional beliefs (especially at higher doses)
- Lightheadedness or fainting (for people with low blood pressure)
- Clumsiness, loss of coordination
- Tiredness, sleepiness
- Racing thoughts (especially at high doses)
- Racing heart, agitation, feeling tense
- Blood-shot eyes
- Dry mouth
- Increased appetite, or “munchies”
- Slowness (for example, slow driving, talking, reaction time)
- Altered sense of time and distance (for example, cars seem like they are moving fast or slow or are further or closer than they are)
- Mild to severe anxiety, including panic attacks or paranoia
- Nausea, especially when combined with alcohol, some prescription drugs or other hallucinogens8
- Weekly or more frequent use is associated with decreased likelihood in graduating high school and ongoing cognitive and academic impairments for at least 28 days after last use
- Daily or near-daily marijuana users are more likely to have impaired memory lasting a week or more after quitting
- Use is associated with the development of psychotic symptoms, including schizophrenia, and the association increases with usage
- Firsthand and secondhand marijuana smoke irritates the lungs since it contains the same cancer-causing chemicals as tobacco smoke. People who smoke marijuana daily or near-daily may have a daily cough, bronchitis, mucus or wheezing.9
Those who first use marijuana before age 15 are almost 13 times as likely to be addicted to marijuana than those who began using marijuana at age 21 or older.
Research has shown that 90% of addictions begin with misuse in the teen years. Our teen years are critical to our personal development and the introduction of drugs at this time often alters that development. That is why it is important to wait, if you use it at all; the older you get the less prone you are to addiction.
Legal Risks with Marijuana - Colorado’s Laws Regarding Marijuana
In Colorado, recreational cannabis became legal as of early 2014 for those 21 and older. Adults are allowed to grow plants and regulated businesses can grow and sell cannabis, its concentrates, and edibles.
Use of marijuana in public is still against the law as is driving under the influence of marijuana.
For those of us still under 21, getting caught with marijuana can involve fines, public service hours, misdemeanor/felony charges and even possible loss of driver’s license.
1https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2241751/
3 https://www.colorado.gov/cdphe/marijuana-health-report
4 www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana/marijuana-addictive
6 http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/241436.php
7 https://www.colorado.gov/cdphe/marijuana-health-report
8 https://www.colorado.gov/pacific/marijuana/immediate-health-effects
9 https://www.colorado.gov/cdphe/marijuana-health-report
10 http://protectwhatsnext.com/consequences